Gluteus Medius Tear
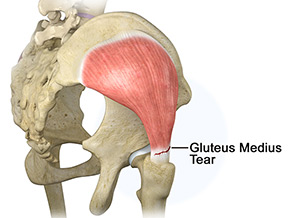
A gluteus medius tear is a condition characterized by severe strain on the gluteus medius muscle that results in partial or complete rupture of the muscle.
The gluteus medius is one of the major muscles of the hip and is essential for movement of the lower body and keeping the pelvis level during ambulation. The gluteus medius muscle arises from the top of the pelvic bone and attaches to the outer side of the thigh bone or femur at the greater trochanter by the gluteus medius tendon. The muscle functions as a hip abductor, controlling side to side movement of the hip and providing stabilization to the joint. Gluteus medius tears often occur at the tendonous attachment to the greater trochanter of the femur bone.
Causes of Gluteus Medius Tear
The tear or rupture of the gluteus medius muscle is commonly seen in runners and athletes involved in high-impact sports such as soccer or basketball. It can occur from sudden bursts of activity and poor flexibility of the gluteus muscle. Any traumatic or overuse injury, or degenerative changes can also lead to partial or complete tear of the gluteus muscle.
Symptoms of Gluteus Medius Tear
The symptoms of a gluteus medius tear involve pain and tenderness over the lateral aspect of the hip which may be aggravated with activities such as running, climbing stairs, prolonged sitting or walking, and lying on the affected side of the hip. One of the main symptoms of a gluteus medius tear is the presence of trendelenburg sign, evidenced by dropping of the pelvis towards the unaffected side during ambulation from being unable to properly bear weight on the affected limb.
Diagnosis of Gluteus Medius Tear
The diagnosis of a torn gluteus medius muscle starts with a physical examination of the patient including palpation of the affected muscle, testing muscle strength and assessing the walking pattern or gait of the patient. Special tests such as single-leg squat test or positive trendelenburg sign confirms the diagnosis of a gluteus medius tear. MRI or ultrasound may be helpful to view the pathological changes of the muscle.
Treatment of Gluteus Medius Tear
The aim of treatment is to restore the normal function of the gluteus medius muscle. Immediately following the rupture, RICE therapy is initiated and involves:
- Rest
- Ice
- Compression
- Elevation
Medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs and steroid injections may be given to reduce the pain and inflammation. You should use a pillow between your legs when sleeping and avoid positions that overstretch the muscle. Assistive devices such as a cane or crutches may be used temporarily to facilitate pain free ambulation.
Surgical treatment may be recommended to repair a complete, full-thickness gluteus medius tear. The surgery can be performed endoscopically through tiny incisions to reattach the torn tendon back onto the greater trochanter with stitches. This helps to restore strength and function to the gluteus medius muscle.